In the valve industry, ball valves are widely used in various fluid control systems due to their simple structure, excellent sealing performance, and ease of operation. Based on the connection method, ball valves can be classified into threaded ball valves and flanged ball valves.
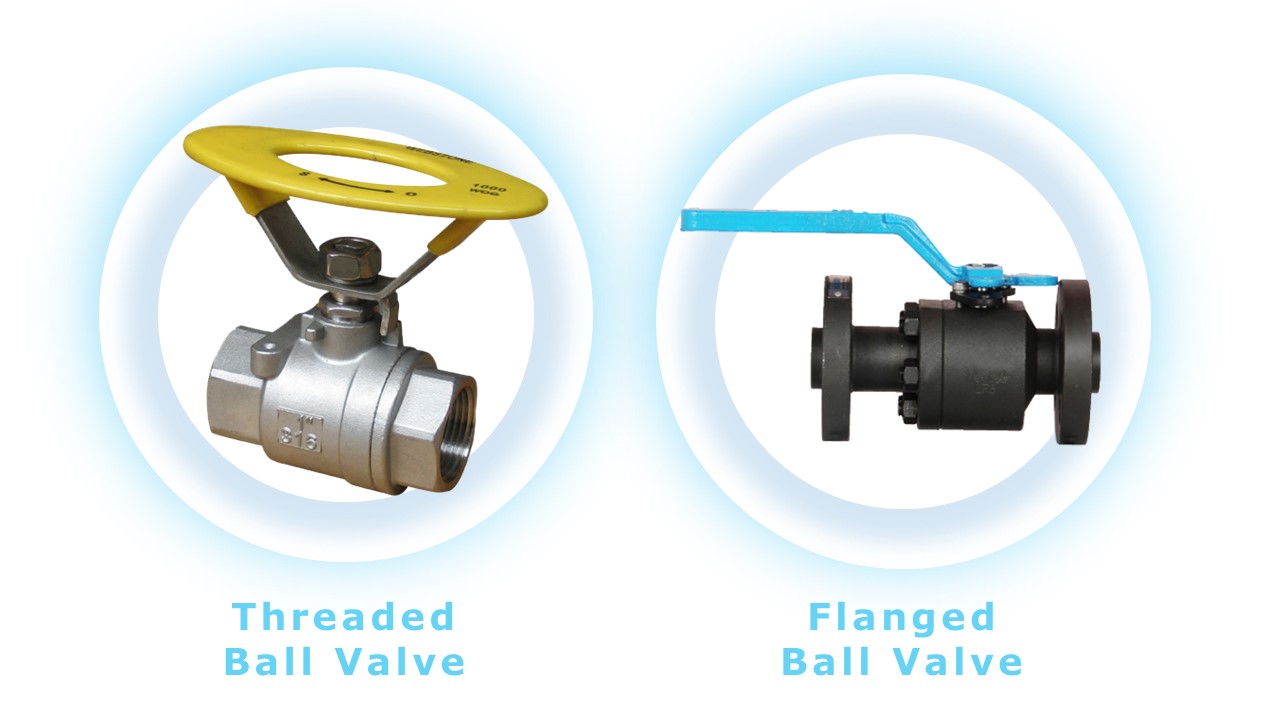
1. Connection Method
Threaded Ball Valves:
Threaded ball valves connect to pipelines using either internal or external threads and are typically used in small-diameter pipeline systems. The advantage of threaded connections lies in their easy installation, compact design, and minimal space requirements, making them especially suitable for confined spaces. Threaded ball valves are commonly used in low and medium-pressure systems and are ideal for fluid control in residential, commercial buildings, and light industrial equipment.
Flanged ball valves are connected to pipelines through flanges and are suitable for medium to large-diameter pipelines. Flange connections offer higher strength and stability, allowing them to withstand higher pressures and temperatures. As a result, they are commonly used in heavy industries, chemical processing, oil, natural gas, and other applications involving high pressure, high temperature, or corrosive media. Flange connections also facilitate easy disassembly and maintenance but require more installation space.
2. Sealing Performance
Threaded Ball Valves:
Threaded ball valves typically use soft sealing materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), offering excellent sealing performance, making them suitable for gases, liquids, and other media. However, under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, threaded connections may pose a risk of leakage, and their sealing effectiveness is generally slightly weaker than that of flanged ball valves in demanding operating conditions.
Flanged Ball Valves:
Flanged ball valves typically utilize metal or composite seals, providing more reliable sealing performance, especially under high-pressure, high-temperature, or corrosive media conditions. The sealing of flange connections is more stable, effectively preventing leakage.
3. Installation and Maintenance
Threaded Ball Valves:
Threaded ball valves are easy to install, requiring only tightening to complete the connection, making them ideal for quick installation in small systems. However, once the threaded connection is secured, it may loosen due to thermal expansion and contraction or vibration of the pipeline, leading to potential leakage risks. During maintenance, if a threaded ball valve needs to be replaced, it may affect the pipeline system and even require reconnection of the entire pipeline.
Flanged Ball Valves:
Flanged ball valve installation requires the use of flanges, bolts, and gaskets, making the installation process more complex. However, flange connections offer higher robustness and reliability. During maintenance, flanged ball valves can be easily disassembled, replaced, or repaired without affecting the entire pipeline system.
4. Cost and Application
Threaded Ball Valves:
The manufacturing cost of threaded ball valves is relatively low, making them suitable for small projects with limited budgets. Due to their compact structure and low cost, threaded ball valves are commonly used in residential water supply systems, small industrial equipment, and light industrial process control applications.
Flanged Ball Valves:
The manufacturing and installation costs of flanged ball valves are higher, but their durability and reliability make them the preferred choice for demanding operating conditions. They are suitable for medium to large-scale engineering projects in industries such as petrochemicals, power generation, shipbuilding, and metallurgy. Flanged ball valves are particularly common in systems that require frequent disassembly and maintenance.